Coksart- This is osteoarthritis of the hip joint.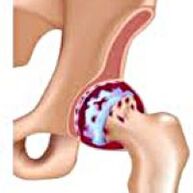 It gradually develops, susceptible to progress for several years, can be one and double -sided.It is accompanied by pain and restriction of movements in the joint.In the later stages, the atrophy of the hip muscles and the shortening of the limbs are observed.The diagnosis is determined on the basis of clinical symptoms and radiography results.Conservative treatment in the early stages of coxarthrosis.With the destruction of the joint, especially in patients in young and middle age, surgery (endoprosthetics) is shown.
It gradually develops, susceptible to progress for several years, can be one and double -sided.It is accompanied by pain and restriction of movements in the joint.In the later stages, the atrophy of the hip muscles and the shortening of the limbs are observed.The diagnosis is determined on the basis of clinical symptoms and radiography results.Conservative treatment in the early stages of coxarthrosis.With the destruction of the joint, especially in patients in young and middle age, surgery (endoprosthetics) is shown.
General information
Coksart rose (osteoarthrosis or deforming arthrosis of the hip joint) is a degenerative-dystrophic disease.It usually develops at the age of 40 and older.It can be a result of various injuries and common illnesses.Sometimes it occurs for no apparent reason.Coksartrose is characterized by a gradual progressive course.Conservative treatment methods are used in the early stages.In the later phases, the common function can only be restored surgically.
In orthopedics and traumatology, coxarthrosis is one of the most common osteoarthritis.The high frequency of its development is due to a significant strain on the hip joint and the widespread prevalence of innate pathology - common dysplasia.Women suffer from coksart more often than men.
The causes of coksart rose
The primary (for unknown reasons) and secondary (developed diseases) of the hip joint are differentiated.
Secondary coksart rose can be the result of the following diseases:
- Hip joint dysplasia.
- Congenital dislocation of the thigh.
- Pertes' diseases.
- Aseptic necrosis of the thigh head.
- Infectious lesions and inflammatory processes (e.g. arthritis of the hip joint).
- Injuries (traumatic transfers, fractures of the hip snack, pelvic fractures).
Coksartrose can either be one of them or are double.With primary coxarthrosis, an accompanying lesion of the spine (osteochondrosis) and knee joint (gonar rose) is often observed.
Risk factors
The factors that increase the likelihood of developing coxarthrosis include:
- Constant increased stress on the connection.Most often observed in athletes in people with an excess body weight.
- Circular disorders, hormonal changes, metabolic disorders.
- Pathology of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis) or stop (flat feet).
- Older and Senile age.
- A sitting lifestyle.
Coksartenrose itself is not inherited.However, certain characteristics (metabolic disorders, structural features and the weakness of the cartilage) can be inherited by the parents by the child.Therefore, the likelihood of occurring the disease is slightly increased.
Patanatomy
The hip joint is formed by two bones: ileum and femoral.The head of the thigh is articulated with the acetabulum of the Iliac bone and forms a strange "hinge".During the movements, the acetabulum remains motionless, and the thigh head moves in different directions, which ensures flexion, expansion, abduction, bringing and rotation shuttle.
During the movements, the articular surfaces of the bones that are not disabled push relative to each other, thanks to the smooth, elastic and durable hyalink norpels, which covers the cave of the swivel cavity and the head of the thigh.In addition, Hyaline cartilage performs a shock absorption function and is involved in redistribution of the load during movement and walking.
In the articular cavity there is a small amount of articular fluid that plays the role of lubrication and offers the diet of the hyaline cartilage.The joint is surrounded by a dense and strong capsule.Above the capsule there are large thighs and gluts muscles, which supply movements in the joint and together with hyalink norpes are also shock absorbers that protect the joint from injuries with unsuccessful movements.
With coxarthrosis, the articular fluid becomes thicker and viscoser.The surface of the hyaline cartilage dries, loses the smoothness that is covered with cracks.Due to the roughness that has arisen, the cartilage is constantly injured in movements, which leads to a thinning and worsens pathological changes in the joint.As the coxarthritis progresses, the bones begin to deform and adapt to increased pressure.The metabolism in the joint worsens.In the later stages of coxarthrosis, severe atrophy of the muscles of the painful link is observed.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
The main symptoms of the disease are pain in the joint, in inguinal areas, thighs and knee joints.Also with cokesart rose, stiffness of movements and stiffness of the joint, gait disorder, lameness, atrophy of the hip muscles and shortening of the limbs on the side of the lesion are observed.A characteristic feature of coksart rose is a restriction of the kidnapping (for example, the patient is difficult if he tries to sit on a chair).The presence of certain signs and their severity depends on the stage of coxarthrosis.The first and most constant symptom is pain.
AtCoksartrose of the 1st degreeThe patients complain about periodic pain that occurs after physical activity (running or walking longer).The pain is located in the joint, less often in the thigh or in the knee.After the calm it usually disappears.The passage for the kox arthrosis of the 1st degree is not broken, the movements are completely preserved, there is no muscle atrophy.
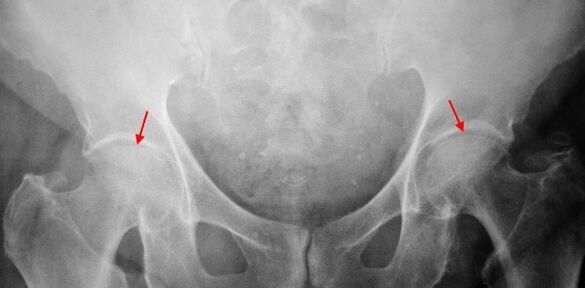
On the patient's X rays, which suffers from coxarthritis of the 1st degree, mild changes are determined: a moderate uneven narrowing of the joint column as well as bone growth around the outer or inner edge of the acetabulum without changes from the head and neck of the thigh.
AtCoksartrose 2 degreesThe pain becomes more intense, often occurs in peace, radiates into the thigh and the groin area.After a significant physical activity, the patient begins to sleep with coksart rose.The volume of the movements in the joint decreases: the abduction and inner rotation of the thigh is limited.
In x radiation images for the coxarthritis of the 2nd degree, a significant narrowing of the common gap (more than half of the normal height) is determined.The thigh head is slightly moved up, deformed and increased, and its contours become uneven.Bone growth with this degree of coxarthrosis occurs not only on the inside, but also on the outer edge of the acetabulum and goes outside the cartilage.
AtCoksartrose 3 degreesThe pain is not only constant and worried about patients during the day, but also at night.Going is difficult if a patient moves with coksart rose is forced to use a stick.The volume of the movements in the joint is very limited, the muscles of the buttocks, the hips and the lower legs are remunerated.The weakness of the distance muscles of the thigh becomes the cause of the deviation of the pelvis in the front level and the shortening of the limb on the aching side.In order to compensate for the shortening, a patient who suffers from coksart rose leans in the painful direction when walking.For this reason, the focus is on the focus, the load on the aching connection increases significantly.
In the case of X -rays for the coxarthritis of the 3rd degree, a sharp narrowing of the joint column, a pronounced expansion of the thigh head and several bone growth is demonstrated.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of coxarthrosis is based on clinical signs and data of additional studies that are radiography.In many cases, X rays enable not only the degree of coxarthrosis, but also the cause of its appearance.For example, the scenes and the flattening of the acetabulum indicate an increase in the neck diaphysical angle, and the form of the proximal part of the femur are indicated that coksart rose is a consequence of the disease or the youthful epiphysissis of pertes.In the case of X -rays of patients with coxarthrosis, changes can also be determined that indicate injuries.
CT and MRI can be used as other methods for instrumental diagnosis of coxarthrosis.Computer tomography enables you to examine pathological changes through bone structures in detail in detail, and the magnetic resonance imaging offers the possibility of evaluating disturbances by soft tissues.
Differential diagnosis
First of all, the coxarthrosis of gonarthrosis (osteoarthrosis of the knee joint) and the osteochondrosis of the spine should be differentiated.The atrophy of the muscles, which occurs in 2 and 3 stages of coxarthrosis, can cause pain in the knee joint, which often expresses lighter than pain in the damage area.Therefore, the examination of the hip joint with the patient's symptoms about the knee pain (inspection, palpation, determination of the movement volume) is the examination of the hip joint and if coxarthrosis is suspected to steer the patient to radiography.
Pain in radicular syndrome (compression of nerve roots) for osteochondrosis and some other diseases of the spine can imitate pain with coxarthrosis.In contrast to coxarthrosis, the pain suddenly occurs after an unsuccessful movement of the roots, after an unsuccessful movement, a sharp curve, lifting weights, etc. in the buttocks and spreads along the back of the thigh.A positive symptom of the tension is determined - severe pain when the patient tries to increase a smooth limb that lies on his back.At the same time, the patient takes his leg to the side, while the kidnapping is limited in patients with coksart rose.It should be taken into account that osteochondrosis and coksart can be observed at the same time, so a thorough examination of the patient is required in all cases.
In addition, the cokesart rose differs with trochanteritis (boot bursite) - aseptic inflammation in the area of binding the gluture muscles.In contrast to coxarthrosis, the disease develops quickly within 1-2 weeks, usually after an injury or a significant physical activity.The pain intensity is higher than with coksart rose.No restrictions on the movements and the shortening of the limb are observed.
In some cases, in the event of an atypical course of the disease or reactive arthritis symptoms that resemble coxarthrosis, can be observed.In contrast to coxarthrosis, these diseases fall the tip of the pain at night.Pain syndrome is very intense and can lose weight when walking.The morning stiffness is characteristic that occurs immediately after waking up and gradually disappears within a few hours.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
The treatment of pathology is involved in traumatologists.The choice of treatment methods depends on the symptoms and the stage of the disease.Conservative therapy is carried out in 1 and 2 stages of coxarthrosis.During the exacerbation of coxarthrosis, injection blocks, non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (pyroxen, indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.) are used.It should be taken into account that drugs of this group are not recommended for a long time, since they have a negative impact on the internal organs and the ability of the hyalin cartilage can suppress them for recovery.
To restore the damaged cartilage for CoksartRose, funds of a group of chondroprotectors (chondroitin sulfate, cartilage extract, etc.) are used.To improve blood circulation and to remove the cramp of small vessels, vasodilaturing medication (tinarisine, nicotinic acid, pentoxifillin, Xanthinol nicotine) are prescribed.According to the information, muscle relaxants are used (muscle relaxation medication).
With the stubborn pain syndrome, patients who suffer from coksart rose can be prescribed intra -card charctions using hormonal medicines (hydrocortisone, triamcinolone, meter).Treatment with steroids must be carried out with caution.In addition, local products are used for coxarthrosis - heating ointments that do not have a pronounced therapeutic effect, but in some cases alleviate muscle pasmeal and reduce the pain due to their "distracting" effect.With coxarthritis, physiotherapeutic methods (bright, ultrasonic therapy, laser treatment, UHF, inductothermia, magnetotherapy), massage, manual therapy and therapeutic gymnastics are prescribed.
The diet for coksart rose has no independent therapeutic effect and is only used as a means of reducing weight.By reducing body weight, you can reduce the load on the hip joints and consequently facilitate the course of the coksart rose.In order to reduce the load of the joint, the doctor can recommend walking with a stick or crutch depending on the degree of coxarthrosis.
In the later stages (with co -arthrosis of the 3rd degree), the only effective treatment method is the operation - which replaces the destroyed joint with an endoprosthesis.Depending on the type of lesion, either individual shells (only replaced the head of the thigh) or two shells (which replaces both the head of the thigh and the swivel hollow) can be used.
The operation of the endoprosthetics for coxarthrosis is planned after a complete examination under general anesthesia.Antibiotic therapy is carried out in the postoperative period.The seams are removed on 10-12 days, according to which the patient is prescribed for outpatient treatment.After the endoprosthetics, rehabilitation measures are necessarily carried out.
In 95% of cases, surgical intervention ensures a complete restoration of the limb function to replace the joint with coxarthrosis.Patients can work, move actively and even do sports.The average lifespan of the prosthesis is all recommendations 15-20 years.After that, a second operation is required to replace a worn endoprosthesis.